Excretory System
Excretion is the biological process by which organisms remove waste products or harmful substances from their bodies. This is essential to maintaining internal balance and preventing harm to the body.
Importance of Excretion
- Prevents the accumulation of waste products that can disrupt normal body functions.
- Maintains the balance of water and salts in the body.
- Eliminates ammonia, a toxic by-product of protein metabolism.
- Removes substances that can be poisonous if left unchecked.
- Ensures the removal of harmful excretory products to keep the body healthy.
The Urinary System
The urinary system is responsible for removing waste and excess substances from the body. It includes the following components:
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
Structure of the Kidneys
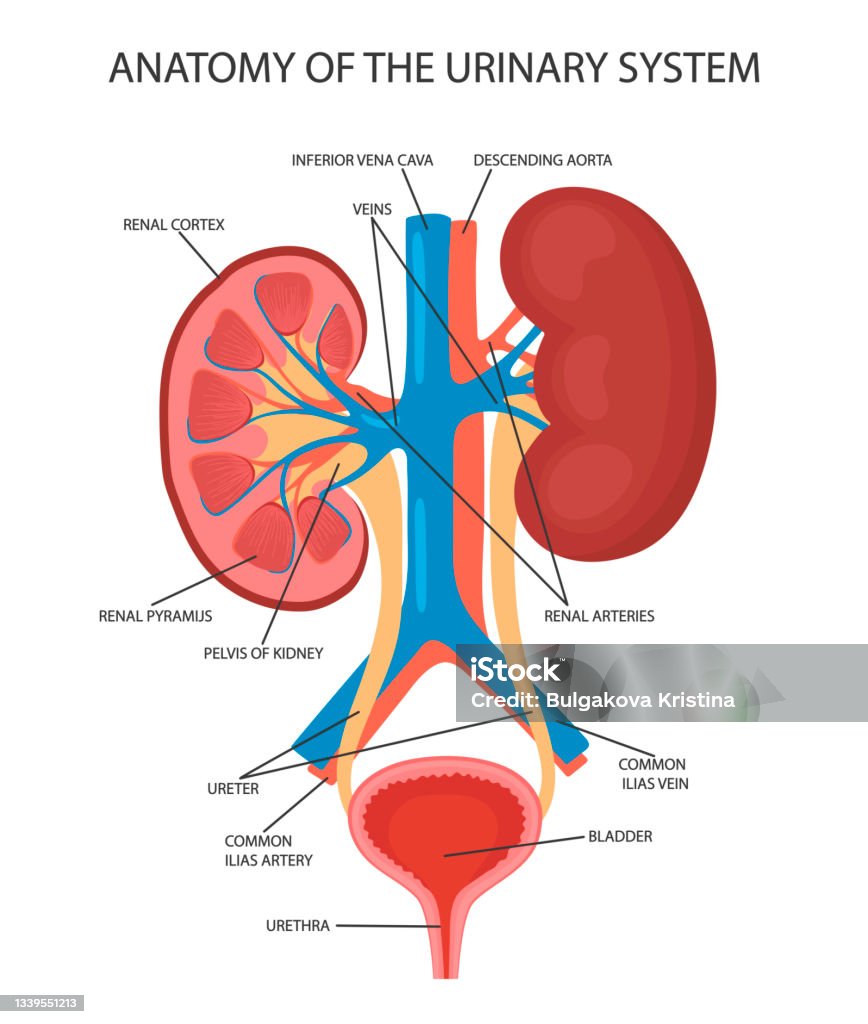
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the lower abdomen. Each kidney has two main regions:
- Cortex: The outer region where nephrons begin.
- Medulla: The inner region containing tubules and pyramids.
Inside the kidney, tubules open into triangular pyramids, which lead to a funnel-shaped cavity called the pelvis. The pelvis connects to the ureter, a tube that carries urine to the bladder. Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and exits via the renal vein.
Nephrons
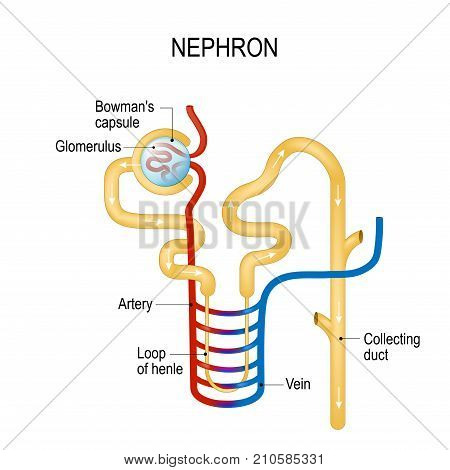
Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron consists of:
- Bowman’s Capsule: A cup-shaped structure in the cortex that receives filtered blood from the glomerulus.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule: A coiled tube in the cortex where selective reabsorption begins.
- Henle’s Loop: A U-shaped loop that extends into the medulla and aids in water and salt reabsorption.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule: A coiled tube in the cortex where further concentration of urine occurs.
Formation of Urine
- Ultrafiltration: Blood enters the glomerulus, and water, urea, salts, glucose, and other solutes are filtered into Bowman’s capsule.
- Selective Reabsorption: Useful substances like water, glucose, and amino acids are reabsorbed into the blood in the proximal tubule and Henle’s loop.
- Hormonal Secretion: In the distal tubule, water reabsorption is controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH), resulting in the formation of concentrated urine.
Other Excretory Organs in Humans
- Lungs: Remove carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are by-products of respiration.
- Skin: Eliminates water, salts, and urea through sweat glands.
- Liver: Processes toxins, such as drugs and alcohol, and excretes them into bile for elimination.
Excretion in Other Organisms
Excretion in Plants
Plants excrete oxygen and water through diffusion via stomata, specialized pores found on leaves, stems, and flowers. Other waste products like oils, latex, and gums are stored in parts of the plant, such as bark or leaves, which are eventually shed.
Excretion in Earthworms
Earthworms use nephridia as their excretory organs. Each segment contains a pair of coiled tubes called nephridia. These tubes collect waste from the coelomic fluid, process it, and expel it through external pores. The nephridia are surrounded by capillaries that help in the exchange of materials.
Excretion in Flatworms
Flatworms excrete waste through a system of longitudinal canals that end in specialized flame cells. Flame cells contain bundles of cilia that create a flickering motion, which helps draw waste into the canals for elimination through pores on the body surface.